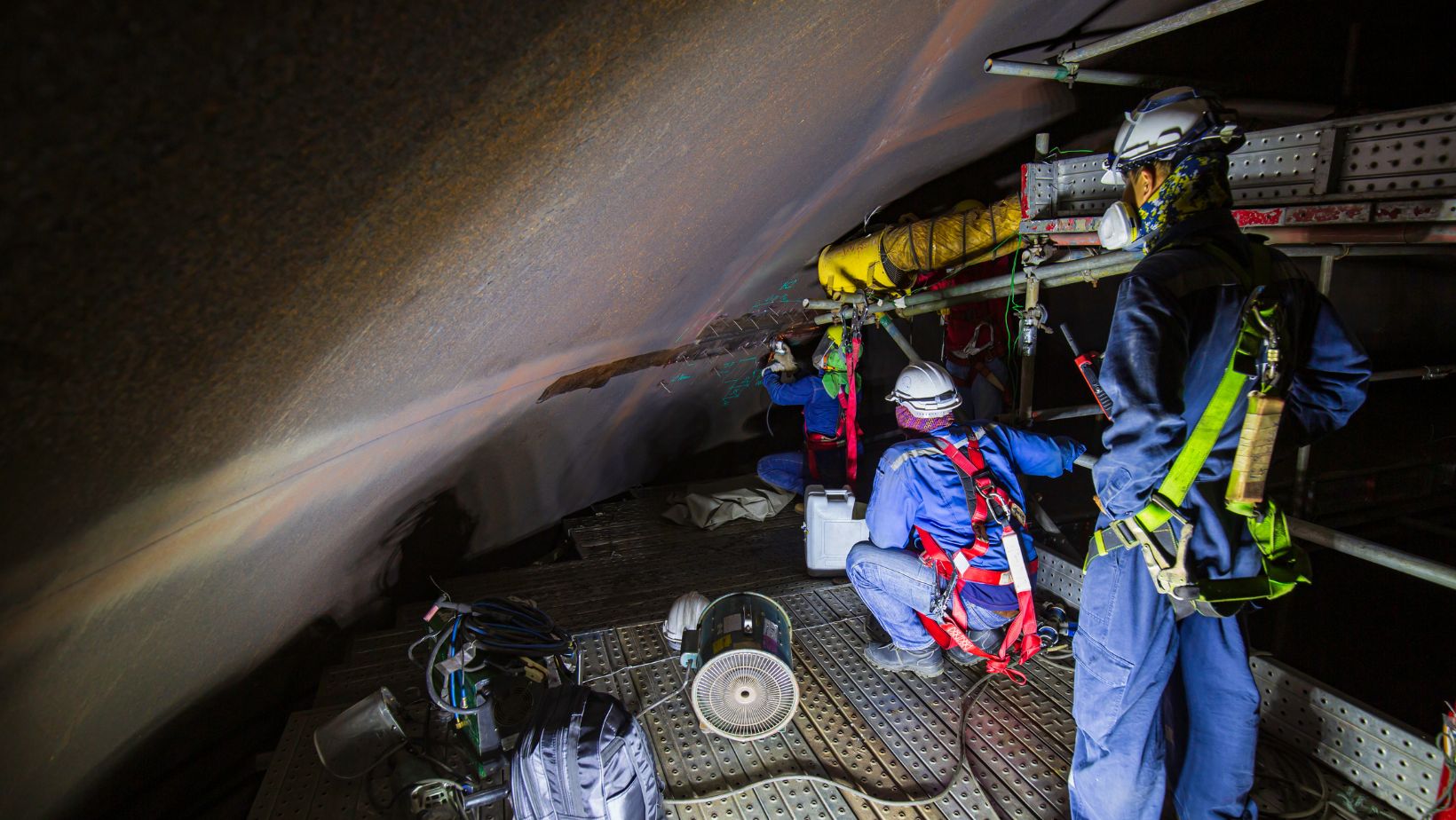
Due to their restricted entry and exit points, confined spaces present particular risks, including the possibility of engulfment, hazardous gases, and inadequate ventilation. In this article, you will explore what you need to know about confined space training.
What is Confined Space Training?
Confined space training is a type of safety training that teaches people how to work safely in small, enclosed areas. These areas, called confined spaces, can be risky because they often have limited entry and exit points, poor ventilation, and may contain hazards like toxic gases or low oxygen levels.
Key Components of Confined Space Training
Confined space training teaches people how to stay safe when working in tight or enclosed spaces. Here are the main things you’ll learn:
Hazard Identification
Toxic gases, low oxygen levels, or physical risks like engulfment or entrapment are examples of potential threats that may exist in cramped areas and must be identified. Trainees learn to identify signs of hazards and understand the risks associated with each type of confined space.
Risk Assessment
Risk assessment is the process of evaluating the likelihood and severity of potential hazards in a confined space. Trainees learn to assess the level of risk posed by various factors, such as the type of confined space, the nature of work to be performed, and the presence of hazardous substances.
Entry Procedures
Entry procedures outline the steps that must be followed before entering a confined space safely. Trainees learn about pre-entry checks, communication protocols, and equipment preparation. Proper entry procedures help minimize the risk of accidents and ensure the safety of workers.
Permit Systems
Permit systems are formal processes that control entry into confined spaces. Trainees learn about permit requirements, including obtaining authorization, completing safety checks, and implementing control measures.
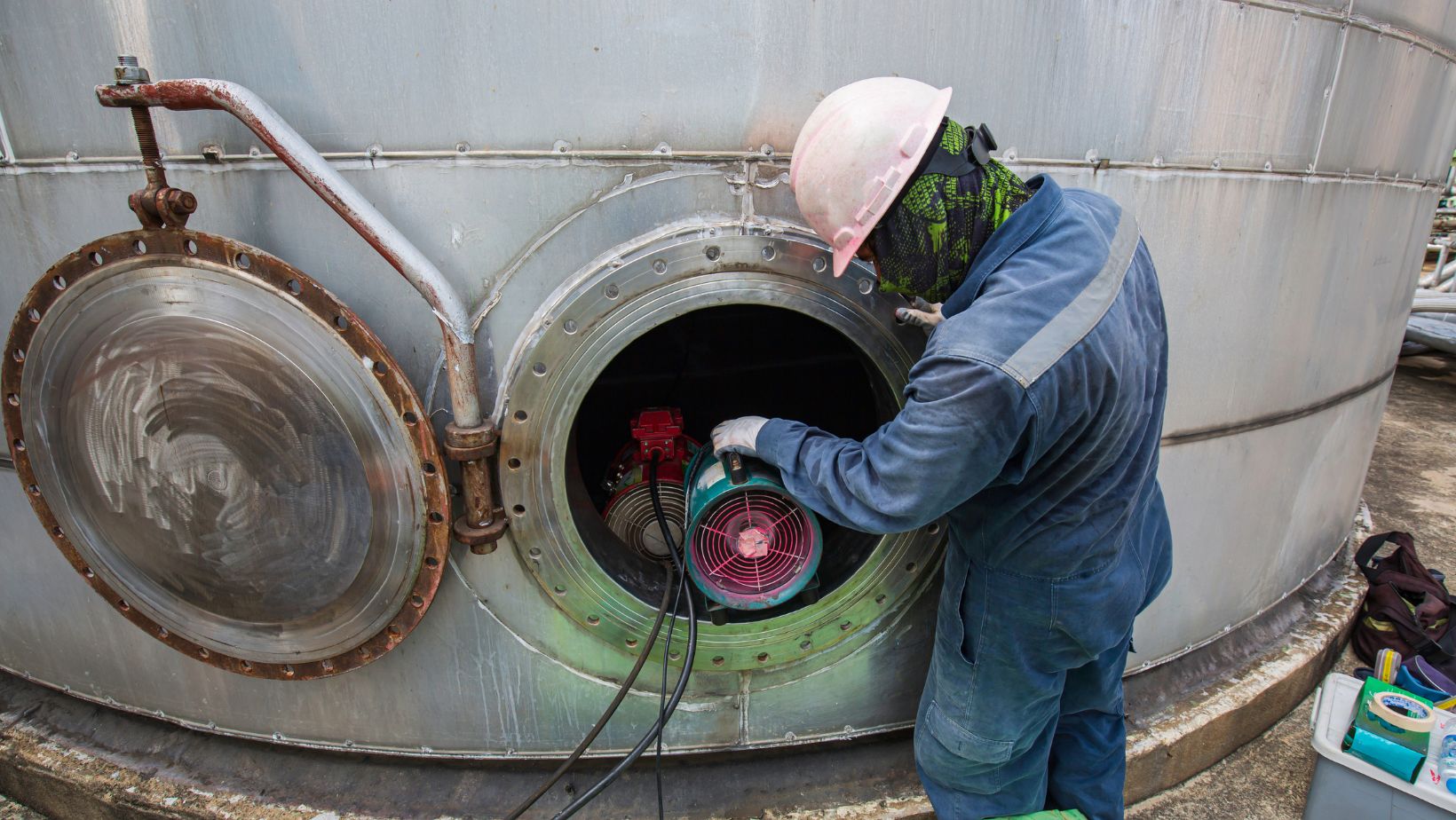

Permit systems help ensure that all necessary precautions are taken before entering confined spaces.
Proper Use of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Trainees learn about the selection, fitting, and use of personal protective equipment (PPE) specific to confined space work. This includes items such as respirators, harnesses, helmets, and protective clothing. Proper use of PPE is essential for protecting workers from hazards present in confined spaces.
Atmospheric Monitoring and Ventilation
Trainees learn to use atmospheric monitoring equipment to assess air quality and detect hazardous gases or low oxygen levels in confined spaces. They also learn about ventilation techniques to control air quality and create a safe working environment.
Emergency Procedures
Emergency procedures cover the actions to be taken in the event of an emergency, such as a gas leak, fire, or medical emergency while working in a confined space.
Trainees learn how to respond quickly and effectively to emergencies, evacuate the confined space, and provide assistance to injured personnel. Emergency preparedness is critical for ensuring the safety of workers in confined spaces.
Training Methods and Resources of Confined Space Training
Classroom Instruction and Theory
Classroom instruction involves traditional teaching methods, where instructors deliver lectures and presentations to trainees in a classroom setting. Trainees learn about confined space hazards, regulations, and safety procedures through theoretical instruction. Visual aids, such as slideshows and videos, may be used to enhance learning.
Hands-On Practical Training Exercises
Hands-on practical training exercises allow trainees to apply theoretical knowledge in real-world scenarios. Trainees practice entry and exit procedures, use of personal protective equipment (PPE), and emergency response protocols in simulated confined space environments. Practical exercises help reinforce learning and develop practical skills.
Online Courses and E-Learning Modules
Online courses and e-learning modules provide flexible training options for individuals who cannot attend traditional classroom sessions. Trainees access training materials, including videos, interactive modules, and quizzes, through online platforms. E-learning allows trainees to learn at their own pace and convenience, making it suitable for remote or self-paced learning.
Use of Simulators
Simulators replicate confined space environments and allow trainees to practice skills and procedures in a realistic virtual setting.
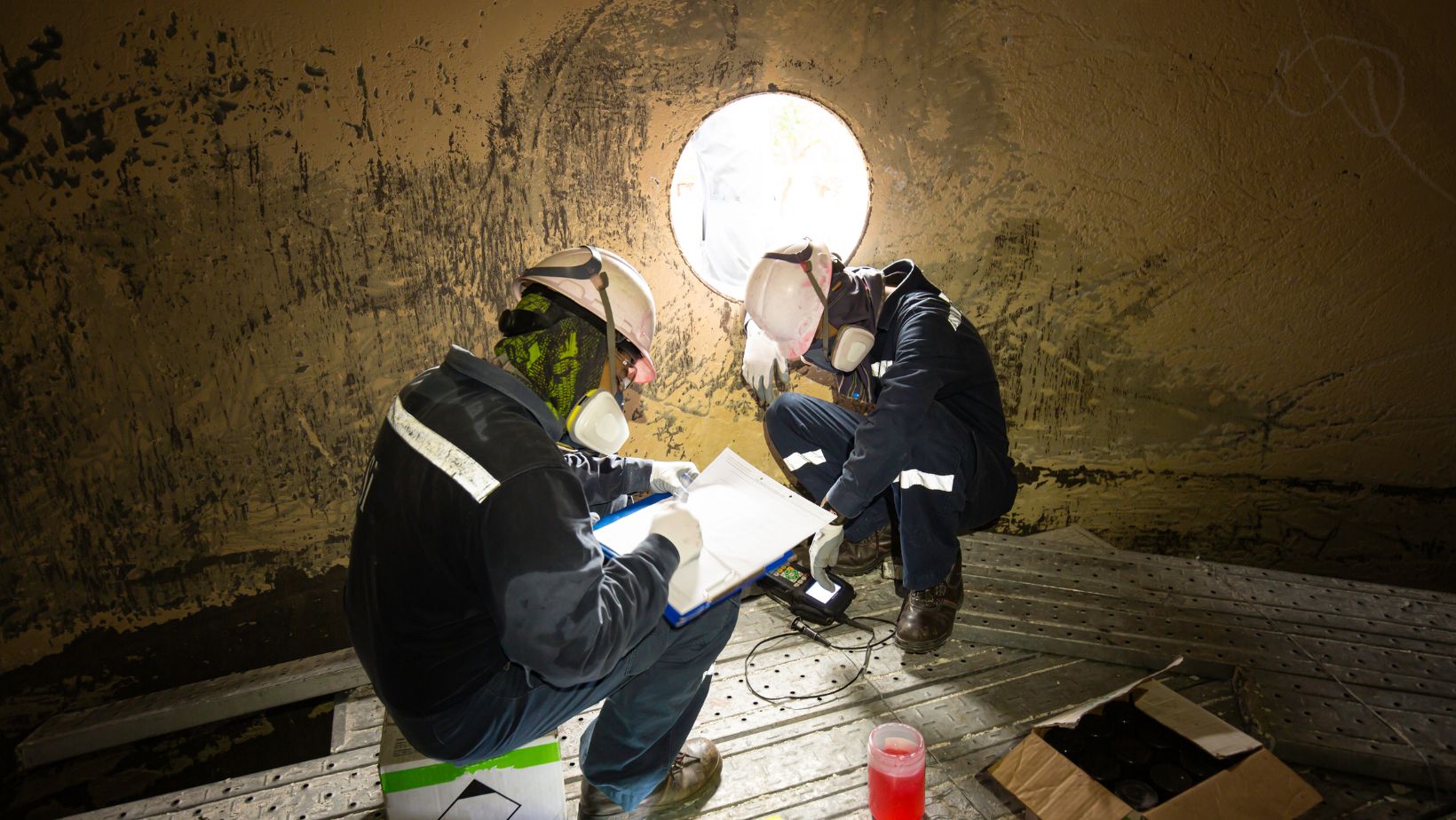

Trainees interact with simulated confined spaces, equipment, and hazards, providing a safe and controlled learning experience. Simulators can simulate various scenarios, allowing trainees to develop problem-solving skills and decision-making abilities in a risk-free environment.
Benefits of Confined Space Training
Confined space training offers several benefits for both employers and workers:
- Increased Safety: The primary benefit of confined space training is improved safety. Workers learn to recognize hazards, assess risks, and use safety equipment effectively, reducing the likelihood of accidents and injuries while working in confined spaces.
- Compliance with Regulations: Many jurisdictions have regulations requiring confined space training for workers who may enter confined spaces as part of their jobs. By providing training, employers ensure compliance with legal requirements and avoid potential fines or penalties.
- Reduced Risk of Accidents: Proper training helps workers understand the dangers associated with confined spaces and how to mitigate risks. This can lead to fewer accidents, injuries, and fatalities, creating a safer work environment for everyone.
Prioritize Safety and Compliance in Confined Space Work
In conclusion, prioritizing safety and compliance in confined space work is essential for the well-being of workers and the success of businesses. So, continue to prioritize safety and compliance in confined space work to create safer, healthier, and more productive work environments for everyone.