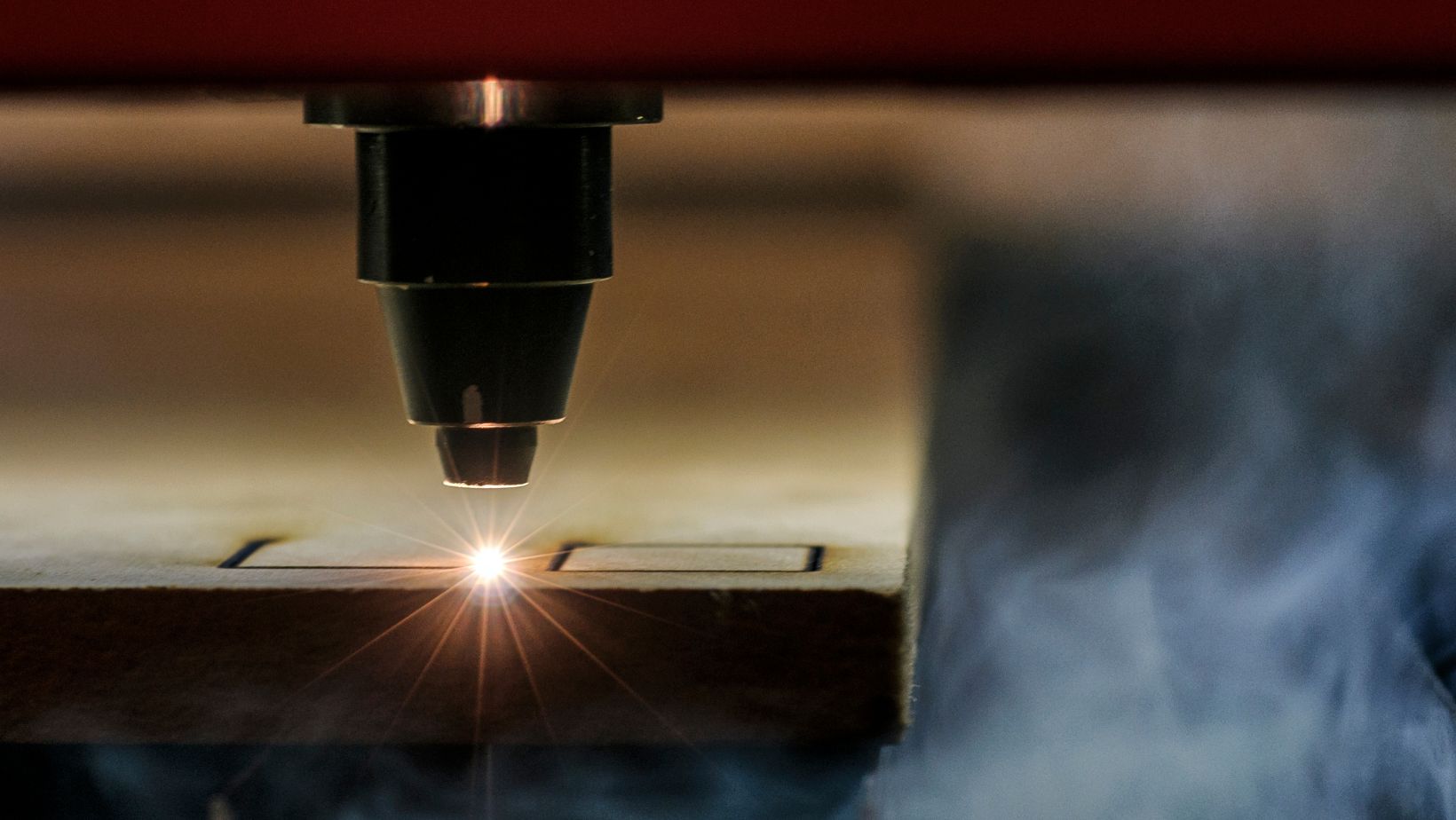
Laser engraving has revolutionized the world of customization, manufacturing, and design, opening up new possibilities across a vast range of industries. Whether you’re crafting intricate jewelry, personalizing corporate gifts, or producing precision components for industrial applications, laser engraving provides a level of detail, efficiency, and flexibility that traditional methods simply can’t match.
At its core, laser engraving uses a focused beam of light to mark or etch the surface of a material. This process removes material with high accuracy, creating designs that are both permanent and highly detailed. One of the greatest strengths of laser engraving is its versatility — it can be used on an impressive variety of materials, including metals, wood, glass, plastics, stone, and even fabrics.
Applications Across Industries
The range of industries benefiting from laser engraving is growing rapidly. In the jewelry sector, for example, artisans use lasers to craft delicate patterns, initials, and logos with stunning precision. The medical industry relies on laser engraving for marking surgical instruments and devices with serial numbers or codes to ensure traceability and compliance. Automotive manufacturers use lasers to add intricate designs or functional markings to dashboard panels and parts.
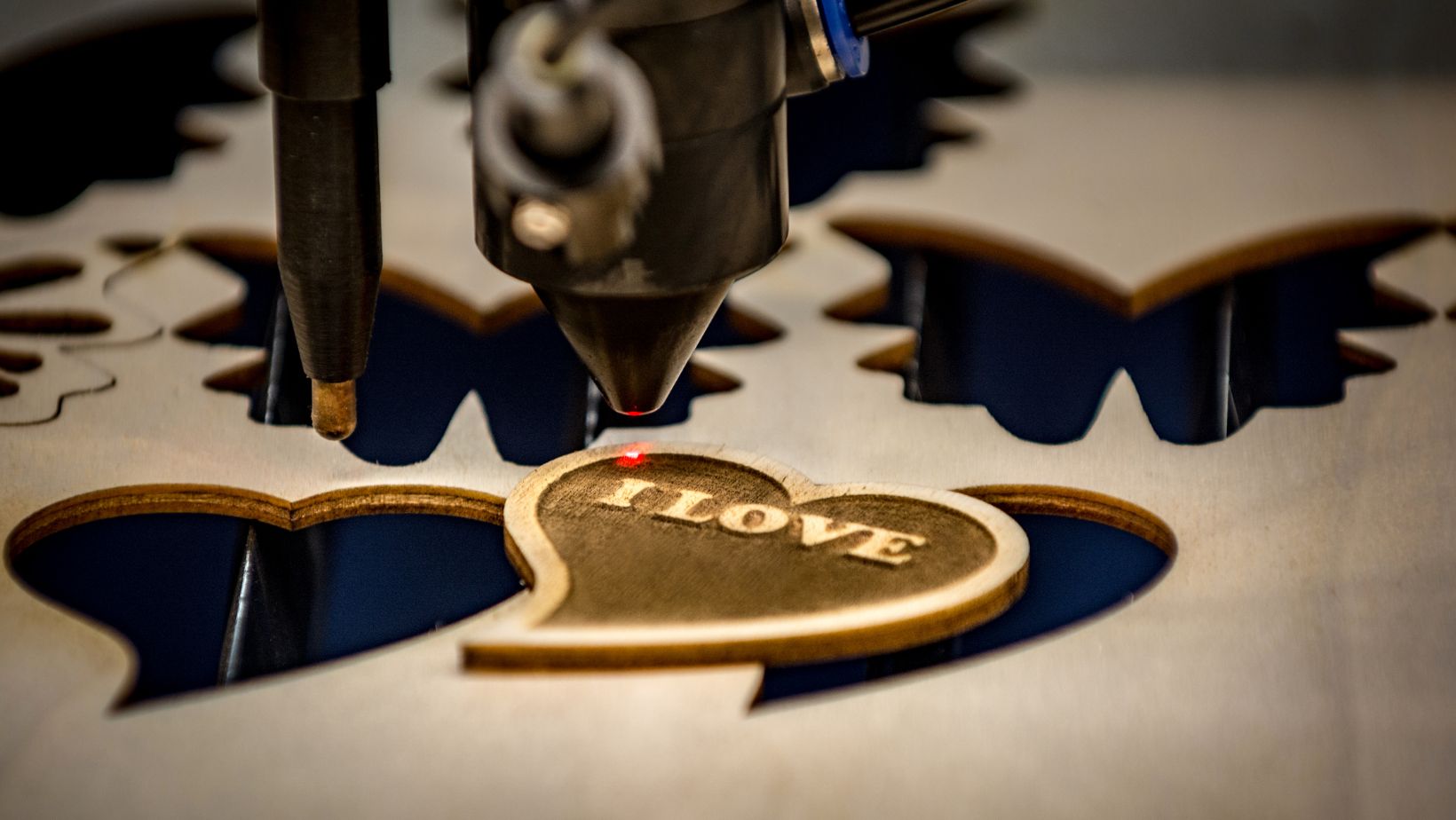

In the world of architecture and interior design, laser engraving is employed to create customized panels, intricate light fixtures, and bespoke furniture pieces. Even in education and research institutions, laser engraving tools are vital for prototyping, model-making, and producing detailed laboratory equipment.
Materials and Techniques
Different materials require different laser settings, but thanks to modern advancements, machines today can be finely tuned to achieve the perfect results. For example, metals like stainless steel or anodized aluminum can be deeply engraved or simply surface-marked, depending on the need. Wood can be beautifully etched to highlight the natural grain, while glass can be frosted with elegant designs without the risk of breakage.
Additionally, laser engraving techniques have expanded to include not just flat surfaces but also cylindrical and irregular shapes. This capability has been greatly enhanced by innovations like the 3D laser engraving machine, which allows for the creation of intricate textures and deep reliefs on a wide range of surfaces. 3D engraving is particularly popular for making molds, sculptures, and high-end custom items where depth and dimension bring added value.
Advantages Over Traditional Methods
Compared to mechanical engraving, laser engraving is non-contact — meaning the laser beam never physically touches the material. This reduces wear and tear on tools and minimizes the risk of damaging delicate surfaces. It also allows for much finer detail and higher repeatability, making it ideal for mass production.
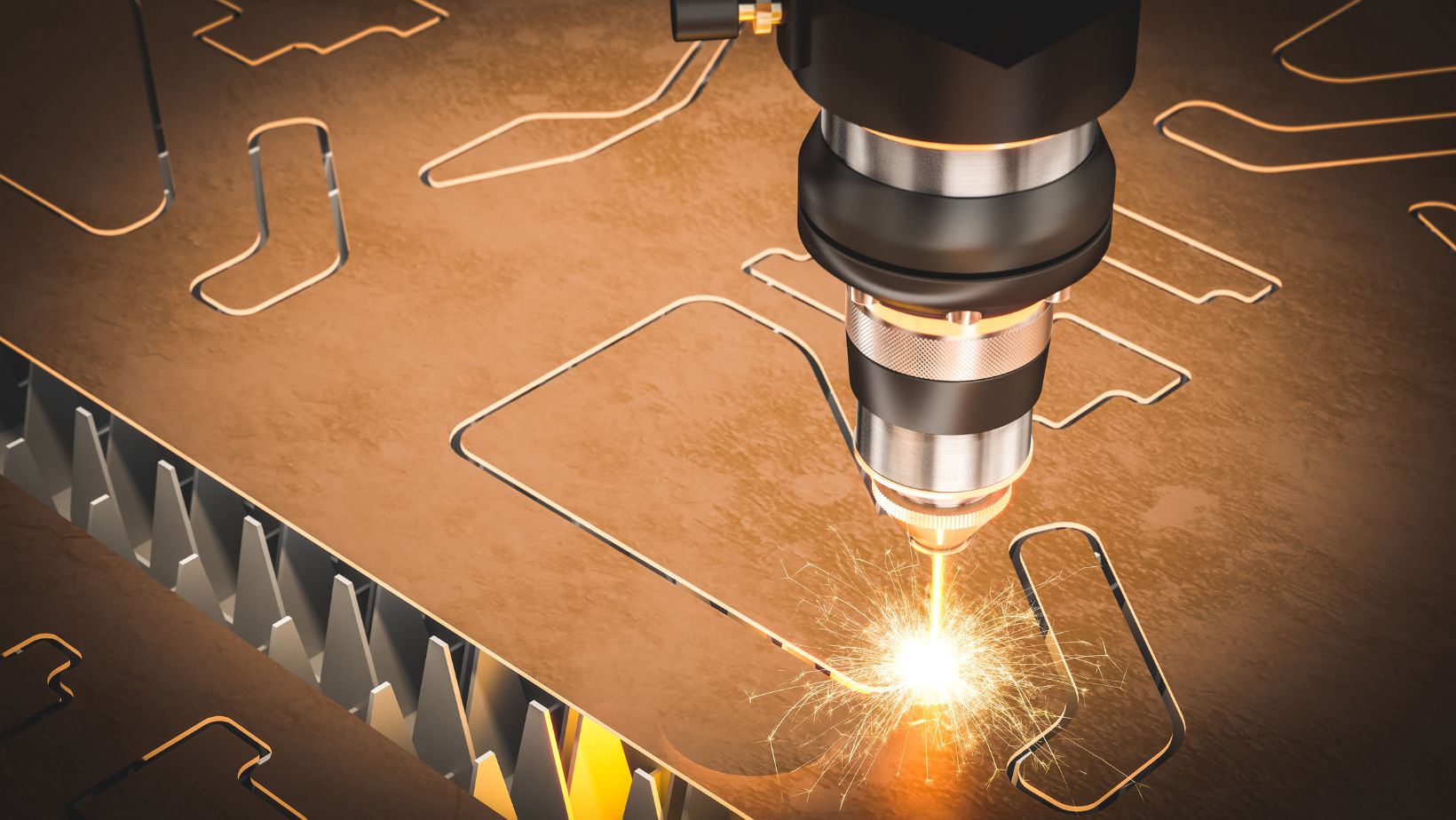

Furthermore, laser engraving is an eco-friendly option. It requires no inks, chemicals, or tool bits that need frequent replacement, resulting in less waste. Modern machines are also highly energy-efficient, making them a greener choice for manufacturers who prioritize sustainability.
Future Innovations
The future of laser engraving looks incredibly promising, with advancements in automation, AI-assisted design, and more powerful, compact laser systems. Personalized products, which continue to be a major trend among consumers, are driving demand for faster, more affordable engraving solutions. Technologies like fiber lasers, CO2 lasers, and UV lasers are becoming more accessible, enabling even small businesses and hobbyists to take advantage of professional-grade equipment.
In particular, the ability to integrate 3D laser engraving capabilities into standard production lines or creative studios is unlocking new levels of customization and craftsmanship. With this technology, artists, designers, and manufacturers can push the boundaries of what’s possible in engraving, creating products that are not only functional but truly works of art.
Conclusion
Laser engraving stands out as one of the most versatile technologies available today. It bridges the gap between art and industry, offering unmatched precision, flexibility, and creative freedom. Whether you’re enhancing a product’s aesthetic appeal, adding vital identification markings, or exploring new artistic possibilities, laser engraving is paving the way for the future of customization and manufacturing.